How To Do Dragon Fruit Farming
Dragon fruit farming (also known as pitaya farming) can be a highly profitable venture if done correctly. Dragon fruit is a tropical cactus that thrives in warm climates and can be grown in various types of soils, but it requires specific care to ensure healthy growth and high fruit yields. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do dragon fruit farming:
1. Site Selection
- Climate: Dragon fruit plants thrive in tropical and subtropical climates. They prefer warm temperatures (25-35°C), and are sensitive to frost. They need full sunlight for at least 6-8 hours a day for optimal growth and fruit production.
- Soil: Dragon fruit plants require well-draining, sandy or loamy soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6 to 7). Heavy, clayey, or waterlogged soils should be avoided.
- Space: A large area is preferable, as dragon fruit vines need space to spread out. Plan for 2-3 meters of spacing between plants.
2. Land Preparation
- Clear the Area: Remove any weeds, debris, and stones from the area where you plan to grow dragon fruit.
- Soil Preparation: Plow or till the soil to a depth of 20-25 cm. You can improve soil quality by adding well-rotted compost or organic matter to enhance fertility and drainage.
- Beds or Raised Rows: Since dragon fruit is a cactus, it's important to plant it in raised beds or rows to prevent waterlogging. This helps improve drainage and root health.
3. Propagation
- Stem Cuttings: Dragon fruit is most commonly propagated through stem cuttings. Take healthy cuttings (approximately 30-40 cm in length) from mature, disease-free plants. Make sure the cutting has at least 2-3 segments.
- Drying the Cuttings: Allow the cuttings to dry for 2-3 days before planting to avoid rotting when they are put into the soil.
- Rooting: Plant the cuttings in well-drained soil or a pot for rooting. Keep the cuttings in a shaded area until they start rooting (around 3-4 weeks).
4. Planting
- Spacing: Plant the rooted cuttings with 2-3 meters of spacing between each plant. This gives enough room for the vines to spread out.
- Planting Depth: Plant the cuttings about 5-10 cm deep into the soil, ensuring that at least 1-2 segments of the cutting are below the soil surface. Water well after planting.
5. Supporting the Plants
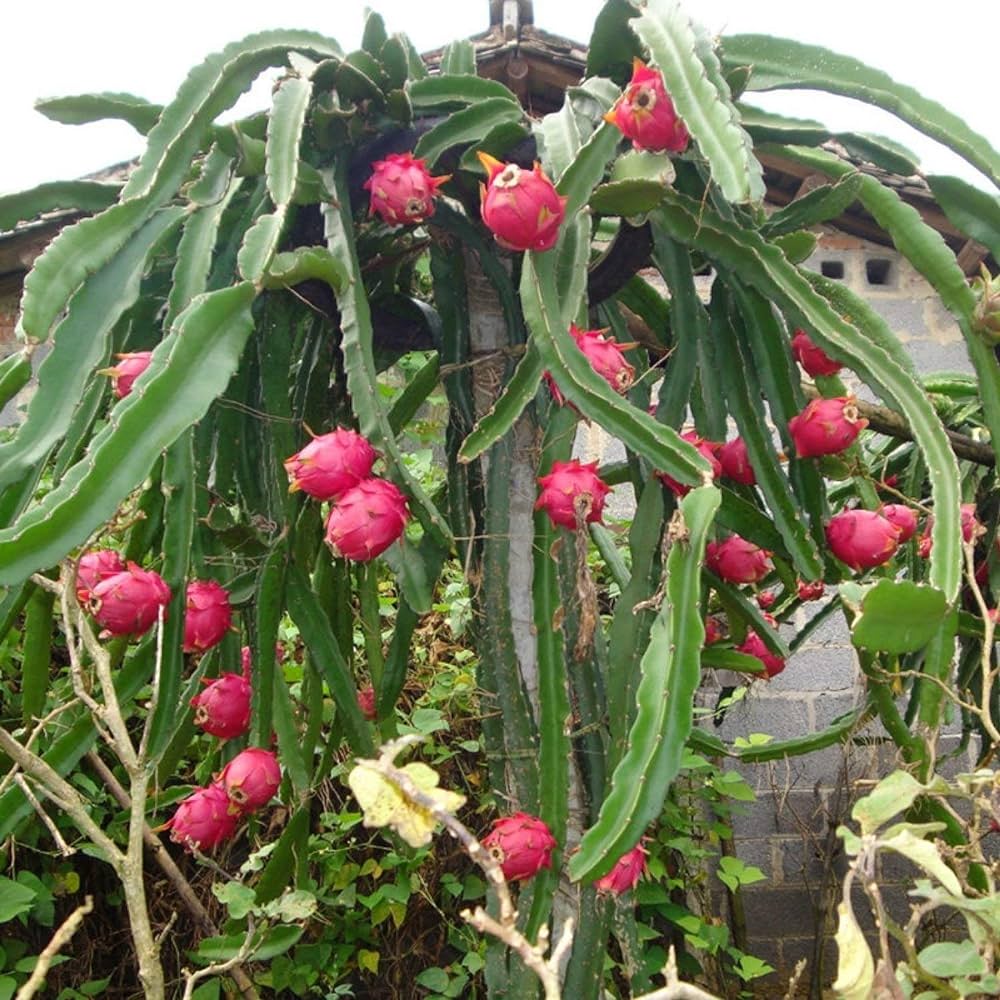
- Trellis System: Dragon fruit plants are climbing cacti and require a sturdy trellis or support structure to grow vertically. Use a strong support like a wooden or metal pole, with wires or strings to allow the vines to climb.
- Trellis Height: A typical support structure can be 1.5-2 meters tall to allow for the plant’s growth and easy harvesting.
6. Watering
- Initial Watering: Water the plants immediately after planting, ensuring the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
- Regular Watering: Dragon fruit requires regular watering, especially during the growing season. However, they are susceptible to root rot if overwatered, so make sure the soil is well-drained. Water the plants 2-3 times a week, depending on the weather conditions.
- Drought Tolerance: Dragon fruit is relatively drought-tolerant, but during flowering and fruiting, adequate moisture is essential for good fruit development.
7. Fertilization
- Organic Fertilizer: Apply well-rotted compost or farmyard manure (FYM) in the planting holes at the time of planting. This improves soil fertility and provides slow-release nutrients.
- Chemical Fertilizers: Use a balanced fertilizer (e.g., NPK 20:20:20) every 2-3 months to promote healthy growth and flowering. During the flowering and fruiting phase, you can use a higher phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (e.g., 10:30:20) to encourage better fruiting.
- Micronutrients: Dragon fruit plants also benefit from micronutrients like magnesium, calcium, and zinc, which help with fruit development.
8. Pruning and Training
- Pruning: Regular pruning is essential to keep the plant healthy and to maintain airflow in the canopy. Trim excess growth, and remove dead or diseased stems.
- Training the Vines: As the vines grow, train them to climb the trellis by tying them gently to the support structure. This helps the plant grow vertically, preventing sprawling and ensuring higher yields.
9. Pest and Disease Management
- Common Pests: Dragon fruit can be affected by pests like ants, mealybugs, aphids, and scale insects. Regularly check the plants for pests and use organic insecticides like neem oil or insecticidal soap if needed.
- Fungal Diseases: Dragon fruit is susceptible to fungal infections like root rot and blight. Ensure proper soil drainage and avoid waterlogging. Fungicides may be used if required.
- Birds and Rodents: Birds and rodents may be attracted to the fruit. Use nets or other protective measures to safeguard the fruit from being eaten.
10. Flowering and Pollination
- Flowering: Dragon fruit plants typically start flowering in the second or third year after planting. Flowers are large and white, blooming at night. Each flower only lasts for one night, so pollination must occur quickly.
- Pollination: Dragon fruit is self-pollinating, but cross-pollination can increase fruit yield. You can encourage pollination by introducing pollinators like bees or by manually transferring pollen between flowers.
- Night Pollinators: In some areas, pollinators like bats or moths assist with pollination at night.
11. Harvesting
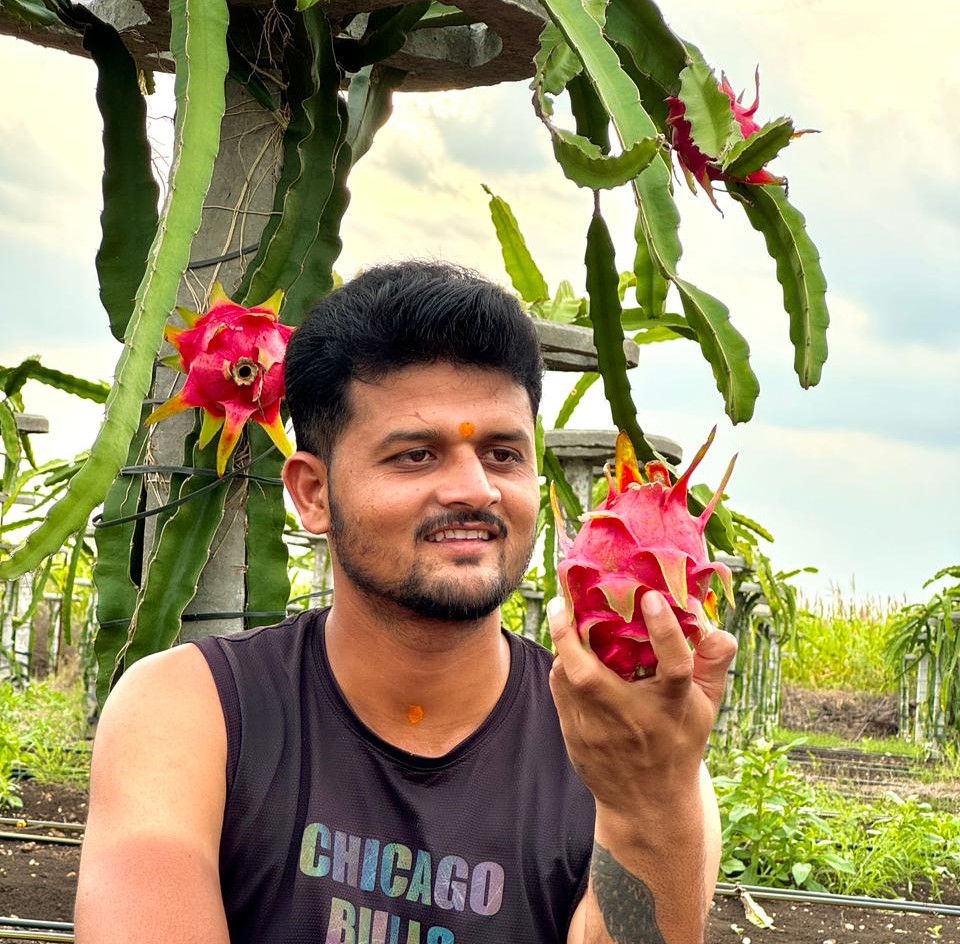
- Fruit Maturity: Dragon fruit usually takes about 30-50 days after flowering to mature. The fruit is ready for harvest when the skin turns from green to bright pink or yellow (depending on the variety).
- Harvesting Method: Gently twist or cut the fruit from the vine to avoid damaging the plant. Be careful not to damage the branches or flowers as it can affect future yields.
12. Post-Harvest Handling
- Storage: Dragon fruit should be stored in a cool, dry place, preferably in a refrigerator, to extend shelf life. Fresh dragon fruit can last 1-2 weeks under proper storage conditions.
- Processing: Dragon fruit can also be processed into juices, dried fruit, jams, or ice cream for added value.
13. Market and Profit
- Selling Fresh Fruit: Dragon fruit has a high market demand due to its exotic appeal and health benefits. It is sold fresh in supermarkets, local markets, and through online stores.
- Value-added Products: You can also increase profitability by processing the fruit into various products like juices, dried fruit, or jams.
Conclusion
Dragon fruit farming can be very profitable with the right care, patience, and investment. The key to successful farming is ensuring proper support for the vines, controlling pests and diseases, and providing the plants with the right soil, nutrients, and water. Once established, dragon fruit plants are relatively low-maintenance and can continue producing high yields for several years, making them an excellent choice for sustainable and profitable farming.